Garhwal seismic Network
Other Laboratories
-
Electron Probe Micro Analyzer (EPMA – CAMECA – SX-100) for quantification of element concentrations in minerals, WD spectra of minerals, and image profiling of elements of mineral.
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma and Atomic Emission Spectrophotometer (ICP-AES-JOBIN YVON JY-70 Plus) – For determination of major, trace and rare earth elements.
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer (ELAN – DRC – E) for determination of major, trace and rare earth elements.
-
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS- Varian-880) with flame and graphite furnace- for determining of major and trace elements.
-
X-Ray Fluorescence Sequential Spectrometer (XRF- Siemens SRS – 3000) – for determination of major and trace elements in rocks/materials.
-
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM- Zeiss EVO 40 with EDAX attachment) – to study the surface morphology of microfossils, minerals and ore minerals.
-
Laser Raman Micro Probe – (Horiba Jobin Yvan – High Resolution) for identification polyatomic species in solid, liquid and gas phases, and for mineral and fluid studies.
-
Seismological Laboratory
Central seismic laboratory of WIHG is at Dehradun where real time seismic data is collected from the remote seismic stations of NW Himalaya. The laboratory is well equipped with the computational facilities to achieve, process and interpret the seismic data in real time mode.
Seismic stations
Presently three seismic networks are in operation in NW Himalaya
-
-
Kangara-Chamba Seismic network
-
Kinnaur Seismic network
GPS stations
There are several permanent GPS stations in the NW Himalaya to monitor geodynamic deformations.
Microzonation
Earthquake risk mitigation is performed for different cities by local site conditions using two methods
-
Multi channel analysis of the shear wave (MASW)
-
Nakamura technique. Microzonation studies have been carried out at Dehradun, Delhi, Chandigarh and Jammu cities.
MPGO
The MPGO is designed to study the earthquake precursors in an integrated manner. The MPGO is equipped with Overhauser magnetometer, tri-axial fluxgate magnetometer, magnetotelluric, SG, ULF-band induction coil magnetometer, radon data-logger, water-level recorders and is backed by the dense network of broad-band seismometers (BBS) and Global Positioning System (GPS).
Magnetotelluric (MT)
Magnetotellurics (MT) is a natural-source, electromagnetic geophysical method of imaging structures below the earth’s surface. These naturally occurring electromagnetic signals induce currents inside the Earth. Simultaneous measurement of electric field and magnetic field time variation at the surface of earth allow estimation of resistivity with depth. Depth of penetration of EM signal is inversely related with the frequency of EM. WIHG is having two broad band MT for imaging lower and upper crustal structures and four LMT (Long period magnetotelluric) for imaging full thickness of lithosphere.
HIMSELP
Himalaya School Earthquake Laboratory program (HIMSELP) has been carried out in 58 schools of northern India to provide awareness and training for school children.
-
-
GPS Laboratory
Microscopy and Image Processing Lab
-
Various Stereo- Binocular Microscopes
-
Image Analysis Systems
Micropaleontology Lab
-
Acid Digestion Chamber
-
Wet Sieving and Oven drying facility
Palynology Lab
-
Distillation plant
-
Palynological Microscopes with image analysis system attachments
Vertebrate Paleontology Lab
-
Air blast and Pneumatic tools
-
-
Microscopes and Instrumentation laboratory
-
Polarizing Microscopes
-
Laser Particle Size Analyzer
-
-
Sedimentology Laboratory
-
Vibratory sieve shakers and Laser Particle Size Analyzer
-
Clay mineral slide preparation
-
Loss on ignition and insoluble residue determination, Centrifuge unit
-
Distilled water plant
-
Fume hood unit
-
-
Thermo-luminescence and OSL Dating Laboratory
-
Dark Room for sample preparation
-
Three Riso TL-OSL DA-20 systems for luminescence dating
-
-
Palaeomagnetism Laboratory
-
Alternating Field Demagnetizer (AFD)
-
KLY/3S Magnetic Susceptibility Bridge
-
JR6/A Spinner Magnetometer
-
Mospin Mini Spinner Magnetometer
-
Isodynamic Separator
-
-
Remote Sensing Laboratory
The laboratory is equipped with the following :
-
Mirror Stereoscopes (for Air Photo interpretation)
-
Large Format Tracing facilities
-
Digital Image Processing facilities
-
-
Geotechnical Laboratory
Geotechnical Laboratory is equipped with basic instruments needed for the characterization of Index properties of soil and rocks required for the landslide studies, like Direct Shear Test Apparatus, Atterberg Limit Apparatus, Unconfined Compressive Strength Test Apparatus, Slake Durability Apparatus, Schmidt Hammer, Total Station and Apparatus for the measurement of P and S- wave velocity (ultrasonic velocity) of rocks in the laboratory under normal pressure and temperature.
-
Glaciology Laboratory
The lab is well equipped with instruments required for the glaciological studies and analysis of field data, particularly for mass balance, hydrology, glacial sediments snow/ice chemistry, ice flow and ice thickness measurements, etc. There is a field station at an altitude of 3800 m and data on various aspects of glacier studies is being collected round the year.
The laboratory at WIHG is equipped with the following.
-
Electronic Distance Meter (EDM): used for topographic survey, stakes measurement for mass-balance studies and snout fluctuation.
-
Ground Penetrating Radar Survey (GPR): used for estimating the ice thickness of the glacier, bed rock topography and total snow accumulation/ablation in a budget year.
-
Sieve Shaker: used for grain size analyses of suspended sediments, moraines and supra, sub and englacial sediments.
-
Automatic Weather Station (AWS): Installed on the Chorabari glacier to collect meteorological data round the year.
-
Steam Drill Machine: used for stake networking ( drill duo to 12m) for mass balance and flow measurement.
-
-
Water Chemistry Lab
Analytical Test Unit (ATU) at Water Chemistry Lab (WCL), WIHG
Physical Parameter testing (Conductivity, Total Dissolved Solids, pH)

HACH HQ40D multipara meter kit for these measurementsAlkalinity Test Facility (ATF/Dissolved carbon di oxide/DIC) at WCL
Alkalinity of Water
-
Alkalinity measures the water's ability to neutralize acids and bases, known as its buffering capacity.
Sources
-
Alkalinity comes from chemicals like bicarbonates, carbonates, and hydroxides, as well as from rocks, land, precipitation, and runoff.
Levels
-
For domestic water, alkalinity should be less than 100 ppm, while the recommended range for drinking water is 30 to 400 ppm.
Measurement
-
Alkalinity is measured through titration with sulfuric acid.
Influence
-
It is affected by changes in pH, temperature, and pressure.
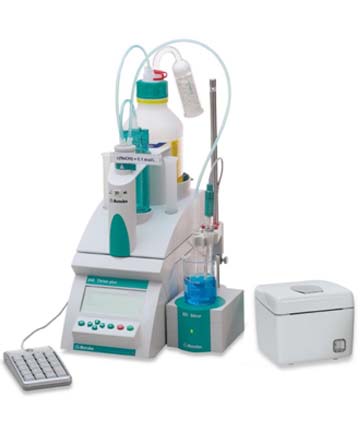
pH based auto-titrator @WCLMajor Ions Test Facility (MITF) @ WCL
Major ions in water are positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions) that contribute to the salinity of water. Some of the most common major ions in water include:
-
(Ca+2) : One of the most abundant cations in water.
-
Magnesium (Mg+2) : One of the most abundant cations in water.
-
Sodium (Na+) : One of the most abundant cations in water.
-
Potassium (K+) : One of the most abundant cations in water.
-
Bicarbonate (HCO3─) : One of the most abundant anions in water.
-
Chloride (Cl─) : One of the most abundant anions in water .
-
Sulfate (SO4─2) : One of the most abundant anions in water.
-
Nitrate (NO3─) : A major ion in natural waters that can contaminate drinking water supplies.
-
Carbonate : An inorganic ion that can significantly impact water treatment processes.

Thermoscientific ICS-6000 at WCL, WIHGStable isotopes (Oxygen and Hydrogen) Test Facility (SITF) in waters @ WCL
Hydrogen
The two stable isotopes of hydrogen that occur naturally in water are 1H and 2H, also known as deuterium. 1H has one proton, while 2H has one proton and one neutron. On average, one out of every 6,420 hydrogen atoms are a deuterium isotope.
Oxygen
The three stable isotopes of oxygen that occur naturally in water are 16O, 17O, and 18O. 16O and 18O are the most abundant and can be easily measured by mass spectrometry.
The stable isotope ratios of hydrogen and oxygen in water are used to study the water cycle, including:

LWIA L2140-i IsotopeMachine WCL, WIHGTracing water sources:
-
The isotopic signature of precipitation can be used to distinguish different water components in groundwater, such as river water and precipitation infiltrate.
deuterium concentration of CANCER patent:
-
The δ2H isotope measurements can be used to track the health of cancer patent based on deuterium concentration.
Measuring catchment processes:
-
The δD and δ18O isotope ratios can be used to measure catchment water balance and key catchment processes.
-
-
Structural Lab
Various Polarized Microscopes
-
Experimental Structural Lab
Biaxial-Uniaxial Press
-
Dendochronlogy Laboratory
-
LINTABTM 6 Tree-ring station: For measurement of Tree-ring width and tree ring analyses using TSAP software.
-
Stereo Binocular Microscope
-
Belt sander: Motorized sanding belt for polishing tree cores.
-


